

For HTTP requests, the MessageBodyReader is used to map an HTTP request entity body to method parameters. Query parameters are extracted from the request URI query annotation is used to specify the MIME media types of representations a resource can consume that were sent by the annotation is used to specify the MIME media types of representations a resource can produce and send back to the client: for example, annotation is used for anything that is of interest to the JAX-RS runtime, such as MessageBodyReader and MessageBodyWriter. URI path parameters are extracted from the request URI, and the parameter names correspond to the URI path template variable names specified in the class-level annotation is a type of parameter that you can extract for use in your resource class. The behavior of a resource is determined by the HTTP method to which the resource is annotation is a type of parameter that you can extract for use in your resource class. The Java method annotated with this request method designator will process HTTP HEAD requests. The behavior of a resource is determined by the HTTP method to which the resource is annotation is a request method designator and corresponds to the similarly named HTTP method.

The Java method annotated with this request method designator will process HTTP DELETE requests. The Java method annotated with this request method designator will process HTTP PUT requests. The Java method annotated with this request method designator will process HTTP POST requests. The Java method annotated with this request method designator will process HTTP GET requests. For example, you could ask for the name of a user and pass it to the application as a variable in the URI: annotation is a request method designator and corresponds to the similarly named HTTP method. You can also embed variables in the URIs to make a URI path template. Table 29-1 Summary of JAX-RS Annotations annotation's value is a relative URI path indicating where the Java class will be hosted: for example, /helloworld. Further information on the JAX-RS APIs can be viewed at. Table 29-1 lists some of the Java programming annotations that are defined by JAX-RS, with a brief description of how each is used.
#Restful web services annotations example archive#
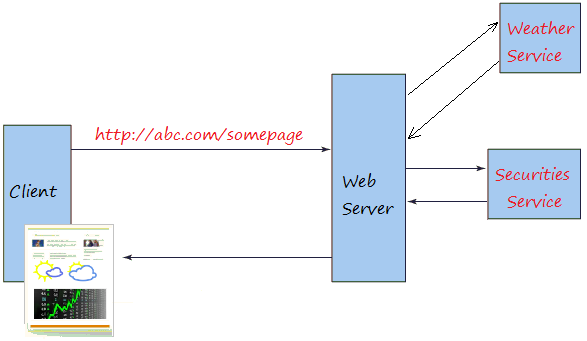
A Java EE application archive containing JAX-RS resource classes will have the resources configured, the helper classes and artifacts generated, and the resource exposed to clients by deploying the archive to a Java EE server. JAX-RS annotations are runtime annotations therefore, runtime reflection will generate the helper classes and artifacts for the resource. Developers decorate Java programming language class files with JAX-RS annotations to define resources and the actions that can be performed on those resources. The JAX-RS API uses Java programming language annotations to simplify the development of RESTful web services. JAX-RS is a Java programming language API designed to make it easy to develop applications that use the REST architecture. 29.2.1 Developing RESTful Web Services with JAX-RS


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
